When trying to conceive leads to frustration, unraveling the infertility causes becomes a priority.
From hormonal dysfunctions to structural barriers and lifestyle choices, numerous factors can disrupt fertility. Let’s embark on a detailed examination of these issues, aiming to bring clarity and hope to your journey toward parenthood.
Key Takeaways
- Infertility, which impacts roughly 1 in 6 globally, has diverse causes ranging from hormonal imbalances and physical reproductive issues to lifestyle and environmental factors.
- Medical conditions and treatments, including STIs, chronic diseases, and cancer treatment, can contribute to or cause infertility; early diagnosis and preventive care are crucial.
- There are various treatments for infertility including lifestyle changes, medication, surgical interventions, and assisted reproductive technologies like IVF and IUI.
Exploring the Roots of Infertility


It’s an unfortunate reality that for many, the path to parenthood is not as straightforward as one might hope. Infertility, defined as the inability to conceive despite having regular, unprotected sex for at least a year, can be a result of a range of factors. Understanding these factors is the first step toward addressing the issue and finding a solution that works for you.
From hormonal imbalances that disrupt ovulation and sperm production, to physical issues involving the reproductive organs, and lifestyle or environmental influences, the causes of primary infertility are multifaceted. Examining the roots of infertility can shed light on these factors and their potential impact on your fertility journey.
Hormonal Factors That Affect Ovulation and Sperm Production
Reproductive processes, from the growth and release of an egg from the ovary to preparing the uterine lining for implantation, are largely orchestrated by hormones during the menstrual cycle. However, hormone imbalances can throw a wrench in this finely tuned system, disrupting critical processes and leading to infertility.
Conditions such as Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) and anovulation can lead to irregular or absent ovulation, thus impairing fertility in women. Similarly, hormonal imbalances in men can manifest through symptoms like erectile dysfunction and low sperm count, contributing to male factor infertility. Diagnostic tools such as LH tests in women and men, testosterone assessments, and measures of ovarian reserve can help identify and understand the extent of hormonal imbalances that affect fertility.
Physical Causes: From Fallopian Tubes to the Male Reproductive System
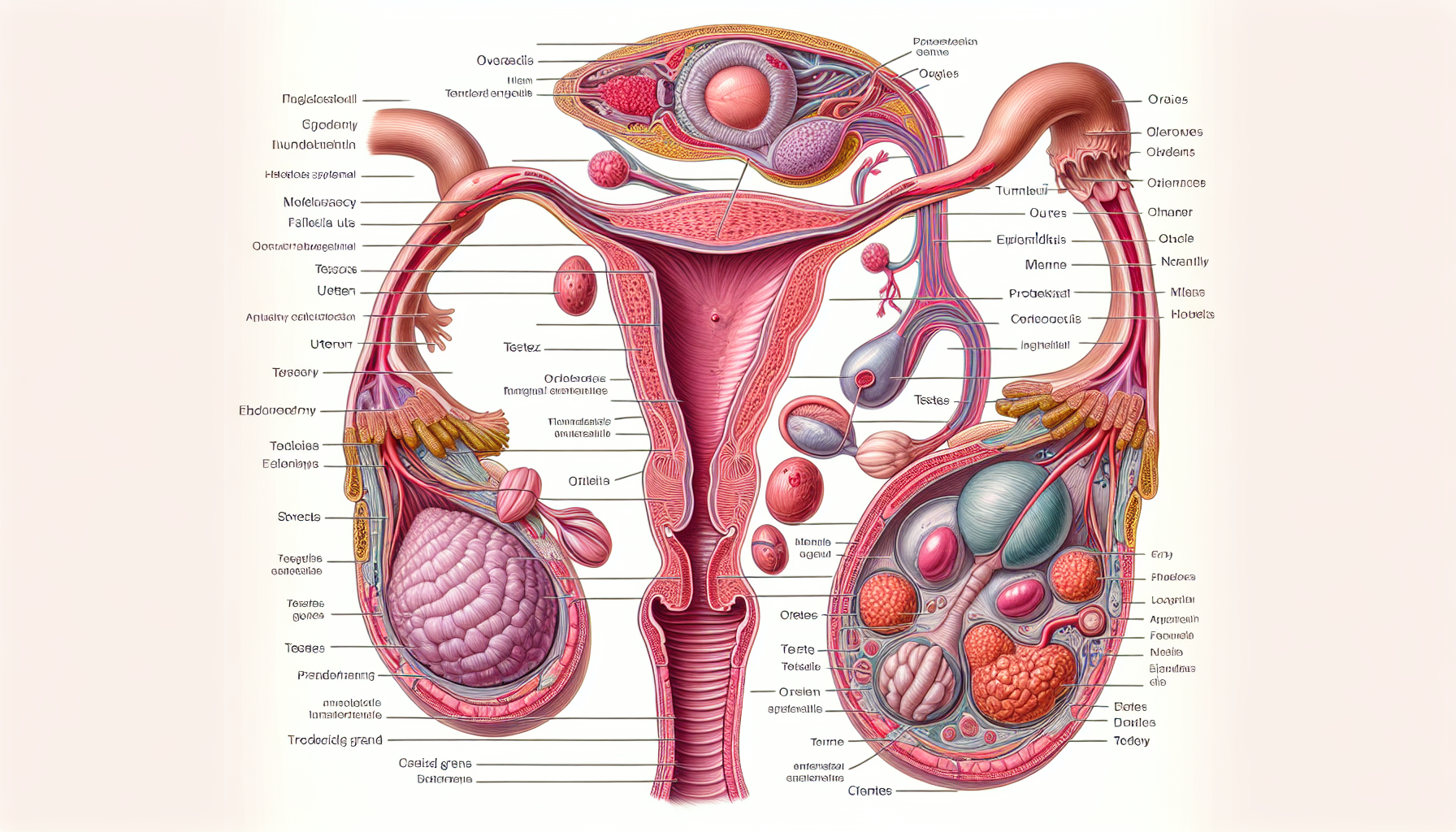


Physical issues in both male and female reproductive systems can contribute to fertility problems. With female infertility, these problems can be quite diverse, ranging from blockages in the fallopian tubes to conditions such as endometriosis and fibroids.
For instance, tubal factor infertility, where a blockage in the fallopian tubes prevents the egg and sperm from meeting, accounts for about 25-30% of all infertility cases. Also, conditions like endometriosis and uterine fibroids can cause fertility issues by causing inflammation and scarring that can prevent ovulation and block the fallopian tubes.
Lifestyle and Environmental Influences on Fertility



Our daily habits and environment can significantly influence fertility, whether we realize it or not. Some risk factors that can significantly influence fertility include:
- Obesity
- Underweight
- Strenuous physical labor
- Excessive exercise
- Smoking
- Heavy drinking
It’s important to be aware of these factors and make necessary changes to improve fertility.
Furthermore, our environment isn’t always our friend when it comes to fertility. Exposure to environmental toxins, heavy metals, and even regular night shifts can negatively impact our reproductive health, making it harder to conceive naturally and reducing the success rate of in vitro fertilization (IVF).
The Impact of Medical Conditions and Treatments on Fertility
Medical conditions and treatments can leave a lasting impact on a person’s fertility. For instance, conditions like diabetes and thyroid disorders can interfere with normal menstrual cycles and ovulation, creating challenges for women trying to conceive. In men, conditions like Low Testosterone can detract from sexual desire and function, and treatments aimed at Low T might interfere with sperm production, potentially causing infertility.
Sexually Transmitted Infections and Pelvic Inflammatory Disease



Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are often overlooked when discussing infertility, but they play a significant role. Infections such as:
- Chlamydia trachomatis
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae are leading causes of tubal factor infertility. Lesser-known infections like:
- Mycoplasma genitalium
- Trichomonas vaginalis have also been implicated in pelvic inflammatory disease and secondary infertility.
Untreated STIs can lead to severe consequences such as chronic pelvic pain, ectopic pregnancy, and infertility, underlining the critical role of timely diagnosis and treatment. In particular, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), often resulting from STIs, can cause significant scarring and blockages within the fallopian tubes, ultimately preventing the passage of eggs and leading to infertility.
Long-Term Health Issues and Fertility
Fertility can often be indirectly affected by long-term health issues. For instance, diabetes can impair fertility by:
- Inducing hormonal imbalances
- Contributing to oxidative stress
- Altering the endometrial environment, which affects implantation and the success of pregnancy.
Moreover, thyroid disorders, including hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism, can interfere with normal menstrual cycles and ovulation, creating challenges for women trying to conceive. In men, conditions like celiac disease can affect fertility by altering testosterone levels and causing changes in sperm structure and motility.
The Aftermath of Cancer Treatments
A lasting impact on a person’s fertility can often be the aftermath of cancer treatments. Radiation therapy and chemotherapy can lead to temporary or permanent infertility in both males and females due to potential damage to reproductive organs. The risk of infertility after cancer treatment is dependent on the type and dose of chemotherapy drugs, as well as the location and dose of radiation therapy.
However, it’s not all bad news. Preventative fertility preservation options such as:
- egg freezing
- embryo freezing
- ovarian tissue freezing for females
- sperm freezing for males
are available to safeguard future fertility before beginning cancer treatments.
Diagnosing Infertility: Tests and Procedures
Diagnosing infertility is a critical step towards finding a solution. It involves a combination of thorough medical history evaluation, physical examinations, and a range of tests and procedures. These tests need to assess several factors, including:
- Ovulatory function
- Tubal disease
- Uterine conditions
- Peritoneal conditions
From blood tests and hormone levels to imaging techniques and semen analysis, diagnosing infertility is a comprehensive process. A deeper understanding of these diagnostic tests and procedures can highlight their role in identifying infertility issues.
Blood Tests and Hormone Levels
The diagnosis of infertility largely depends on blood tests and hormone levels. They provide insight into hormone imbalances that might be disrupting critical aspects of reproductive health, such as ovulation and sperm production.
Tests for follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) are conducted to assess egg supply and ovarian function, while estradiol tests measure a form of estrogen to evaluate ovarian function and egg quality. In men, FSH tests evaluate sperm count and are an integral part of the fertility assessment.
Imaging Techniques: Ultrasound and Beyond
Ultrasound and other imaging techniques are vital tools in diagnosing infertility. These techniques allow doctors to examine the reproductive anatomy and detect issues like fibroids, uterine anomalies, and ovarian cysts.
Transvaginal ultrasound is a primary method for detailed evaluation of the uterus and fallopian tubes, while hysterosalpingography, an X-ray based technique, is used to identify fallopian tube obstructions. Collectively, these imaging techniques help paint a clearer picture of potential physical causes of infertility.
Analyzing Semen Quality and Count
Male infertility diagnosis heavily relies on the analysis of semen quality and count. Semen analysis is a vital part of the male infertility evaluation to determine semen volume and sperm production.
The analysis includes various parameters such as:
- Sperm count
- Motility
- Morphology
- Volume
- pH
- Presence of white blood cells
Abnormalities in these parameters can indicate potential infertility, underscoring the importance of comprehensive semen analysis in infertility diagnosis.
Addressing Infertility: Treatment Options and Strategies
Once the roots and causes of infertility are identified, exploring treatment options and strategies becomes the next step. Thankfully, in 85% to 90% of infertility cases, successful treatment is possible with:
- lifestyle modification
- medication
- assisted reproductive technology (ART)
- surgery
The selection of a fertility treatment is influenced by various factors including the root cause of infertility, the age of individuals, duration of trying to conceive, and personal preferences. These fertility treatments range from fertility medications to surgical treatments, and assisted reproductive technologies like in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Surgical Remedies for Reproductive Obstacles
Certain types of infertility can be addressed through surgical remedies for reproductive obstacles. For instance, hysteroscopy allows for the examination and treatment of issues within the uterus, such as the removal of fibroids and polyps, while laparoscopy allows surgeons to view and operate on the reproductive organs, treating conditions such as endometriosis and fallopian tube blockages.
Moreover, procedures like myomectomy are preferred for removing uterine fibroids in women wishing to conceive in the future, focusing on preserving the uterus. Other procedures like radical trachelectomy can preserve fertility in cases of early-stage cervical cancer by removing the cervix and surrounding tissues but keeping the uterus intact.
Assisted Reproductive Technology: IVF and IUI



Assisted reproductive technology (ART) is often at the forefront of fertility treatments. ART entails all fertility treatments involving the handling of both eggs and sperm, with in vitro fertilization (IVF) and related procedures standing out as the principal technologies.
In addition to IVF, other ART procedures like gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT) and zygote intrafallopian transfer (ZIFT) exist. These procedures involve placing gametes or zygotes directly into the fallopian tubes.
Additionally, intrauterine insemination (IUI), also known as artificial insemination, involves directly placing sperm into the uterus to improve fertilization chances.
Navigating Emotional and Mental Health Aspects of Infertility
Infertility is a journey that challenges not only the physical body but also the mind and emotions. Dealing with infertility can often lead to a range of psychological-emotional disorders, such as:
- turmoil
- frustration
- depression
- anxiety
- hopelessness
- guilt
- feelings of worthlessness
Coping with the emotional stress of infertility is crucial for maintaining mental health during the fertility journey. Expressing emotions openly, improving communication with your partner, finding a supportive community, and managing mental health are all vital aspects of navigating the emotional and mental health aspects of infertility.
Fertility Awareness and Preventive Measures
It’s equally important to focus on fertility awareness and preventive measures, in addition to understanding the causes and treatments of infertility. Understanding your body and cycle can significantly increase your chances of conception.
Fertility awareness methods provide ways to track ovulation and fertile days, which can help couples conceive by identifying the most opportune times for sexual intercourse. Similarly, maintaining a healthy weight is critical for fertility, as being significantly overweight or underweight can disrupt ovulation and menstrual cycles, affecting the ability to conceive.
Infertility and Fertility Care: The Global Perspective
Infertility extends beyond being a personal issue and stands as a global health concern. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), one in six people globally experience infertility in their lifetime, signifying a universal health issue.
While the prevalence of infertility is consistent across different income levels, access to fertility care can often be inequitable. Financial constraints are a significant barrier in low and middle-income countries, where direct medical costs for treatments such as IVF often surpass the average annual income. This underscores the need for more accessible data and policies to reduce healthcare expenses and prevent impoverishment due to fertility care costs.
Summary
Navigating the journey through infertility can be an overwhelming experience, filled with complex medical jargon, emotional turmoil, and tough decisions. However, armed with comprehensive knowledge about the causes of infertility, the impact of medical conditions, diagnostic tests and procedures, treatment options and strategies, and the emotional and mental health aspects, you are better equipped to confront this challenge.
Remember, you’re not alone on this journey. There’s a global community of individuals and couples facing similar challenges, and numerous healthcare professionals dedicated to helping you navigate this path. Infertility is not the end of your journey, but rather a detour on your path to parenthood. Stay strong, seek support, and never lose hope.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some of the main causes of infertility?
The main causes of infertility are ovulatory disorders such as PCOS, endometriosis and for men low sperm count or low testosterone. It’s important to seek professional advice if you’re facing challenges with conception.
How do I know if I’m infertile?
If you’re having trouble getting pregnant or staying pregnant, it’s important to consult with a doctor for infertility testing, as there may not be clear symptoms of infertility. However, irregular menstrual periods or no periods in women, as well as hormonal changes in men, could be potential indications of infertility.
Why am I not getting pregnant?
It is possible that irregular ovulation, polycystic ovary syndrome, hormonal imbalances, stress, low body weight, or obesity may be causing difficulty in getting pregnant. Additionally, poor semen quality or fallopian tube issues could also be contributing factors. Getting a diagnosis through testing with a fertility specialist is crucial to save time and worry and understand your next steps towards parenthood.
Why can I get pregnant but not stay pregnant?
It’s possible that irregularly shaped uterus, immune system issues, and hormone abnormalities such as thyroid disease or diabetes could be leading to a difficulty in maintaining a pregnancy. These issues may impact your ability to stay pregnant. It is important to consult a fertility doctor to diagnose any potential issues if you are experiencing recurrent miscarriages.
How are medical conditions and treatments linked to infertility?
Medical conditions like diabetes, thyroid disorders, sexually transmitted infections, and cancer treatments can disrupt normal bodily functions and harm reproductive organs, leading to infertility.
Can fertility issues relate to men as well as women?
Absolutely. It’s generally thought that fertility issues are predominantly due to women, however, 40% of any issue is female related, 40% of any fertility issue is male related and 20% is either both or unexplained. For this reason it is always important that both men and women struggling to conceive should have a fertility test to find out if there are any potential issues preventing a pregnancy. For women under 35, it’s advisable to seek advice from a specialist after one year of trying; and if a woman is 35 or over, it’s important to seek advice after trying to conceive for 6 months.








